OSINT Sources – Using Geolocation for OSINT Investigations

OSINT Sources – Using Geolocation for OSINT Investigations – Learn about Geolocation OSINT, Geolocation Intelligence tools, and OSINT Investigation Techniques
OSINT Sources – Using Social Media for OSINT Investigations

OSINT Sources – Using Social Media for OSINT Investigations – Learn about Social Media OSINT, Social Media Intelligence tools, and OSINT Investigation Techniques
What is the OSINT Framework? – A Complete Guide to the OSINT Framework, Essential Tools, and Best Techniques
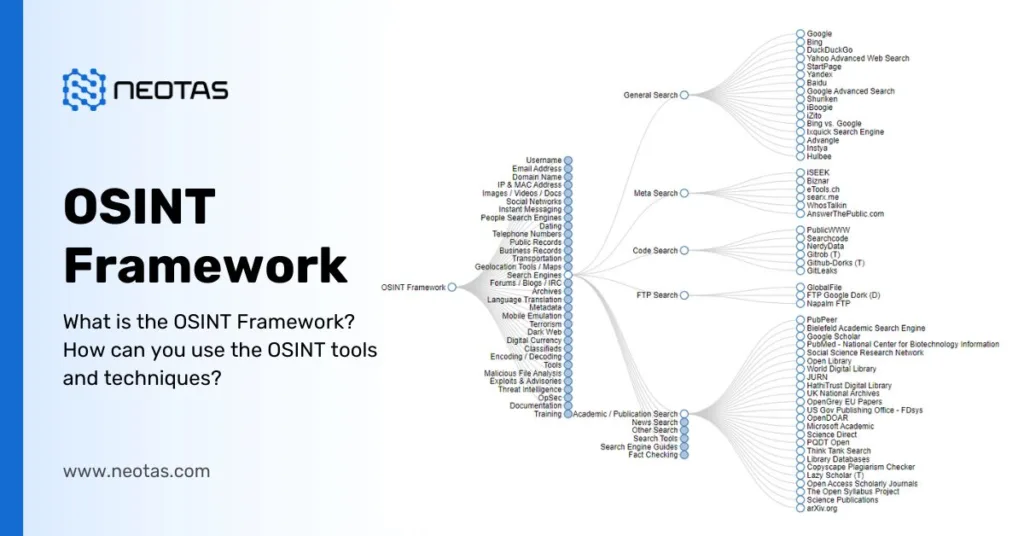
What is the OSINT Framework? – A Complete Guide to the OSINT Framework, Essential Tools, and Best Techniques in 2025 | Neotas UK
The Role of Social Media Checks in Immigration: Enhanced Security and Integration

The Role of Social Media Checks in Immigration Every country in the world is faced with immigration issues. The USA and many European countries are processing increasing numbers of migrants applying for citizenship. In an era dominated by digital connectivity, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, shaping how we communicate, […]
The Power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Social Media Checks and OSINT in Today’s World

Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Social Media Checks and OSINT This article delves into the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on screening processes, specifically within the domains of Social Media checks and Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT). Unveiling the intricacies of AI-driven analyses, it explores the fusion of speed and precision in handling extensive datasets. Emphasising real-world […]
OSINT Framework – Key Components of OSINT Framework and How to use it?

OSINT Framework A comprehensive guide to OSINT framework, OSINT Tools, OSINT Techniques, and how to use it. The OSINT Framework is a comprehensive collection of open source intelligence (OSINT) tools and resources that are organised and categorised for easy access. It’s designed to assist researchers, investigators, cybersecurity professionals, journalists, and anyone else interested in gathering […]
Leveraging AI Chatbots for Enhanced Social Media Checks and OSINT

AI Chatbots for Enhanced Social Media Checks and OSINT In the digital age, information is abundant, but the challenge lies in its verification and analysis. Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) has become a vital tool for individuals, businesses, and governments to gather actionable intelligence from publicly available sources. One of the latest innovations enhancing the OSINT landscape […]
Unveiling the Power of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) Techniques

Open Source Intelligence Techniques In today’s data-driven world, information is power. The ability to access, analyze, and interpret publicly available data has become a cornerstone of decision-making, risk management, and strategic planning. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) techniques have emerged as the catalyst for transforming raw data into actionable insights. This article delves into the intricacies […]
OSINT Risk Assessment – Unveiling Digital Footprints for Due Diligence & Informed Decision-Making

OSINT Risk Assessment Empower your risk assessment strategy with OSINT insights, harnessing publicly available data for proactive decision-making. In the ever-expanding digital landscape, the power of information has become more evident than ever before. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) has emerged as a critical discipline that enables organizations to harness the wealth of publicly available data, […]
A Comprehensive Guide on Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) Tools and Techniques

OSINT Tools and Techniques – The ultimate guide to getting started with Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) and OSINT Technical Sources for Enhanced Due Diligence.
OSINT Techniques – Elevating Open Source Data Gathering and Analysis

OSINT Techniques OSINT techniques encompass a wide range of methods for gathering information from publicly available sources on the internet. These techniques are used to collect, analyze, and interpret data to gain insights, make informed decisions, and perform various investigative activities. In the dynamic realm of information acquisition, Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) techniques stand as […]
OSINT Background Check – What Makes An Expert Background Check from Neotas Different?

OSINT Background Check – Neotas are experts in background screening checks. Learn why Neotas OSINT background check is better than traditional background checks

